

Now, we will specify that we have to use the mysql database using the following command – use mysql Let us first check all the databases using the following command – show databases In MySQL, the table named “user” in the default-created database stores all the information related to users. Let us see the list of users in my MySQL database server. Now, you will see the MySQL shell and work on your database.
#Mysql set root password how to#
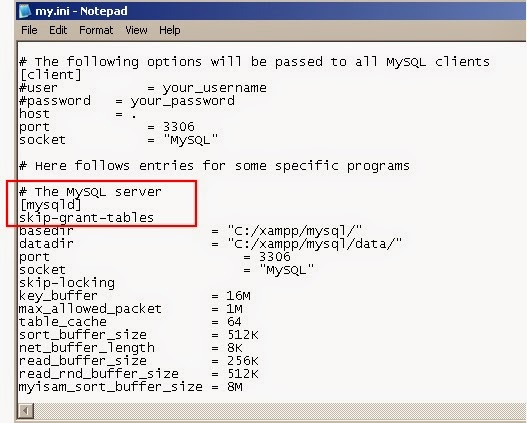
In this article, we will learn how to change or set the password to the root user. It is essential to set strong passwords for your root user from a security standpoint to ensure that the sensitive data stored in your MySQL database remains protected. Further, there might be a situation in which you have forgotten your root password and wish to set the new one, or sometimes you will want to set the root user’s password stronger than the previous one. If this does not happen and you want to set the password for the default root user, you can do so later. During the installation process, MySQL automatically creates a default user named “root” on the machine and prompts the user to set a password for this account. But, when you want to perform database operations that require many higher privileges, you can use the account created by default in MySQL, which has almost all the privileges assigned to it that is the root user. Then when attempting to reset the password I received an error, but googling elsewhere suggested I could simply forge ahead.Multiple users can have different privileges assigned to each of them in the MySQL database. I used the advice of Kevin Jones above with the following -skip-networking change for slightly better security: sudo systemctl set-environment MYSQLD_OPTS="-skip-grant-tables ~]$ mysql -u root The password reset commands are at the bottom of Which takes you to where it mentions the systemctl set-environment MYSQLD_OPTS= towards the bottom of the page. For more information, see SectionĢ.5.10, “Managing MySQL Server with systemd”. On these platforms, mysqld_safe is no longer Sudo systemctl unset-environment MYSQLD_OPTSĪs of MySQL 5.7.6, for MySQL installation using an RPMĭistribution, server startup and shutdown is managed by systemd on Unset the mySQL envitroment option so it starts normally next time Mysql> ALTER USER IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPass' ħ. > WHERE User = 'root' AND Host = 'localhost' Īs mentioned my shokulei in the comments, for 5.7.6 and later, you should use


#Mysql set root password update#
Mysql> UPDATE er SET authentication_string = PASSWORD('MyNewPassword') Update the root user password with these mysql commands Start mysql usig the options you just setĥ. Sudo systemctl set-environment MYSQLD_OPTS="-skip-grant-tables"ģ. So to reset the root password, you still start mySQL with -skip-grant-tables options and update the user table, but how you do it has changed. Systemd is now used to look after mySQL instead of mysqld_safe (which is why you get the -bash: mysqld_safe: command not found error - it's not installed)
#Mysql set root password install#
I have no answer to setting up the root password during installation, but here's what you do to reset the root passwordĮdit the initial root password on install can be found by running grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log There is 2 issues - why can't I log in as root to start with, and why can I not use 'mysqld_safe` to start mySQL to reset the root password. What version of mySQL are you using? I''m using 5.7.10 and had the same problem with logging on as root


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
